Science Source
A new statistical approach to climate change detection and attribution
- Proposes a new statistical approach to climate change detection and attribution that is based on additive decomposition and simple hypothesis testing
- Applies the method to the linear trend in global mean temperature over the period 1951–2010
- Finds that most of the observed warming over this period (+0.65 K) is attributable to anthropogenic forcings (+0.67 ±± 0.12 K, 90 % confidence range), with a very limited contribution from natural forcings (−0.01±0.02−0.01±0.02 K)
Related Content
Headline

Feb 15, 2024 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Amazon Could Reach Tipping Point By Midcentury
Headline

Jan 16, 2024 | Climate Nexus Hot News
2023 Smashes Hottest Year Record
Headline
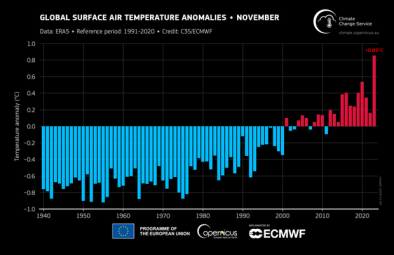
Dec 7, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
It’s Official - 2023 Is World's The Hottest Year On Record
Headline

Dec 7, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Earth Veering Closer To Dangerous Tipping Points


