West Virginia and Virginia Flood June 2016
Once-in-a-thousand year rainfall in West Virginia drove record-breaking flooding in which at least 23 lives were lost. Climate change increases the risk of flooding by increasing the frequency of extreme precipitation. Warmer air holds more water, leading to stronger and more frequent heavy precipitation events, a global trend that has been firmly attributed to climate change. In the northeastern region of the US that includes West Virginia extreme precipitation has increased 71 percent from 1958 to 2012.
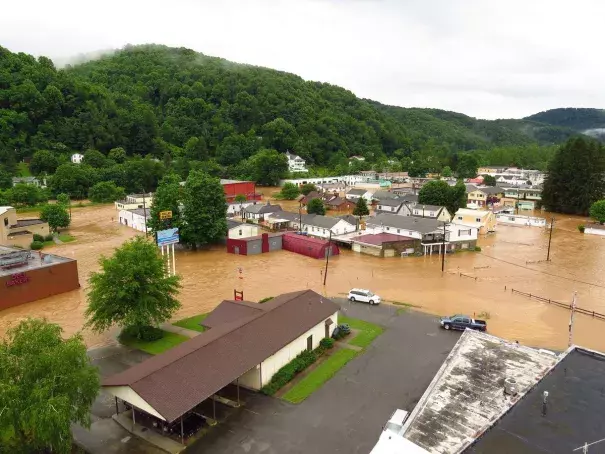

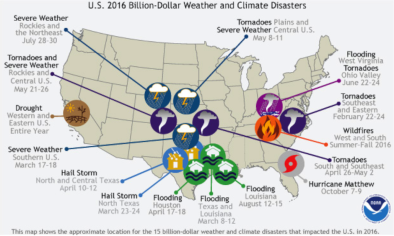


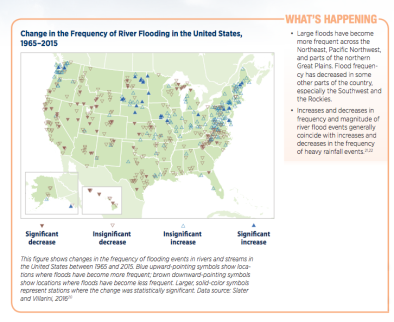
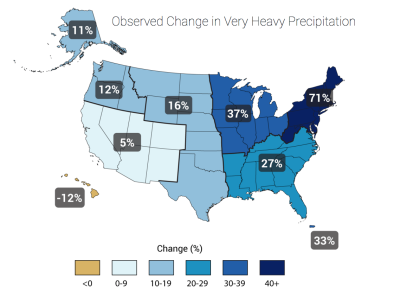
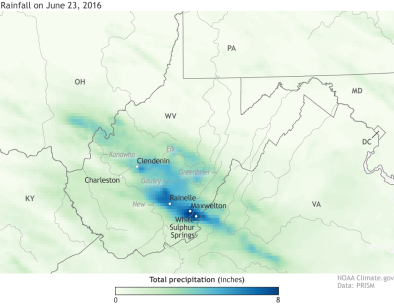
Rare and extreme rainfall inundate West Virginia and Virginia
A powerful storm system, which the National Weather Service called a "nearly 1 in a thousand year event"[1] brought as much as 8 to 10 inches of rain in six to eight hours in parts of West Virginia, killing at least 23 people.[2][3] Gov. Earl Ray Tomblin of West Virginia called the flooding "among the worst in a century" for some parts of West Virginia.[2]
It was the third-deadliest flood on record in West Virginia, according to the West Virginia state climatologist Kevin Law.[3] Only the Buffalo Creek flood in 1972 (when 125 died after a dam break) and a November 1985 flood (when 38 died from a combination of Hurricane Juan's remnants and another storm) killed more in the state, Law said.[3]
On the Jackson River, the water came up about 6 feet in a three hour or span or less coming within a foot of the record level set in 1985 at Covington.[4] Dunlap creek near Covington set a new flood stage record at 16.49 feet.[5]
Extreme rainfall fits with increased heavy precipitation trend in the Northeast
Climate change contributes to increased flooding because warmer air holds more water, leading to stronger and more frequent precipitation events.
In the northeastern region of the US that includes West Virginia extreme precipitation has increased 71 percent from 1958 to 2012.
According to the Northeast chapter of the Third US National Climate Assessment, "In...much of West Virginia...more intense precipitation events will mean greater flood risk, particularly in valleys, where people, infrastructure, and agriculture tend to be concentrated."[6]
At the scale of West Virginia, a relatively small region, it is difficult to quantify the relative factors driving local trends due to the domination of natural variability at the local scale.[7][8] Flooding trends are also complicated in southern West Virginia due to the region's unique topography, which has dictated a somewhat steady regime of flooding events.[9]
Related Content