Iceberg twice size of Luxembourg breaks off Antarctic ice shelf
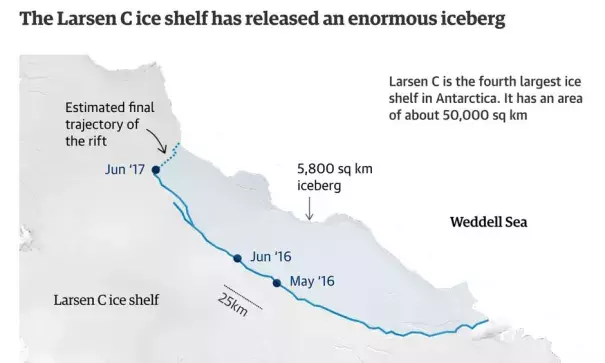
A giant iceberg twice the size of Luxembourg has broken off an ice shelf on the Antarctic peninsula and is now adrift in the Weddell Sea.
Reported to be “hanging by a thread” last month, the trillion-tonne iceberg was found to have split off from the Larsen C segment of the Larsen ice shelf on Wednesday morning after scientists examined the latest satellite data from the area.
The Larsen C ice shelf is more than 12% smaller in area than before the iceberg broke off – or “calved” – an event that researchers say has changed the landscape of the Antarctic peninsula and left the Larsen C ice shelf at its lowest extent ever recorded.
...
[Adrian Luckman, professor of glaciology at Swansea University and leader of the UK’s Midas project] said that while the Larsen C ice shelf might continue to shed icebergs, it might regrow. Nevertheless previous research by the team has suggested that the remaining ice shelf is likely less stable now that the iceberg has calved, although it is unlikely the event would have any short-term effects. “We will have to wait years or decades to know what will happen to the remainder of Larsen C,” he said, pointing out that it took seven years after the release of a large iceberg from Larsen B before the ice shelf became unstable and disintegrated.
What’s more, Luckman stressed that while large melt ponds were seen on Larsen B prior to its collapse - features which are thought to have affected the structure of the ice shelf - those seen on Larsen C are far smaller and are not even present at this time of year.
And while climate change is accepted to have played a role in the wholesale disintegration of the Larsen A and Larsen B ice shelves, Luckman emphasised that there is no evidence that the calving of the giant iceberg is linked to such processes.
Twila Moon, a glacier expert at the US National Ice and Snow Data Center agrees but, she said, climate change could have made the situation more likely.
“Certainly the changes that we see on ice shelves, such as thinning because of warmer ocean waters, are the sort [of changes] that are going to make it easier for these events to happen,” she said.
Related Content