Science Source
Bidimensional Diagnostics, Variability, and Trends of Northern Hemisphere Blocking
- Analyzes Northern Hemisphere winter blocking through the introduction of a set of new bidimensional diagnostics based on geopotential height that provide information about the occurrence, the duration, the intensity, and the wave breaking associated with the blocking
- Performs analysis with different reanalysis datasets in order to evaluate the sensitivity of the index and the diagnostics adopted
- Defines a new category of blocking placed at low latitudes that is similar to midlatitude blocking in terms of the introduced diagnostics but is unable to divert or block the flow
- Finds that over the Euro-Atlantic sector it is possible to phenomenologically distinguish between high-latitude blocking occurring over Greenland, north of the jet stream and dominated by cyclonic wave breaking, and the traditional midlatitude blocking localized over Europe and driven by anticyclonic wave breaking
- Finds these latter events are uniformly present in a band ranging from the Azores up to Scandinavia
- Finds a similar distinction cannot be pointed out over the Pacific basin where the blocking activity is dominated by high-latitude blocking occurring over eastern Siberia
- Analyzes the variability and the trend, considering the large impact that blocking may have on the Northern Hemisphere
- Results show a significant increase of Atlantic low-latitude blocking frequency and an eastward displacement of the strongest blocking events over both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans
Related Content
Event
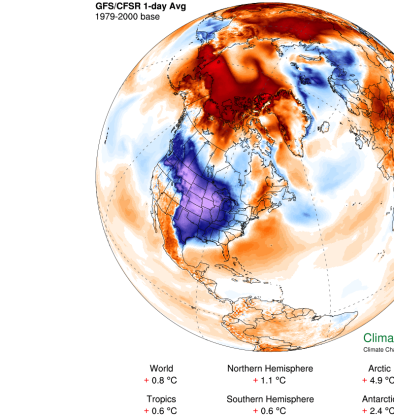
Mar 4, 2019
Polar Vortex Dip and US Arctic Invasion March 2019
Headline
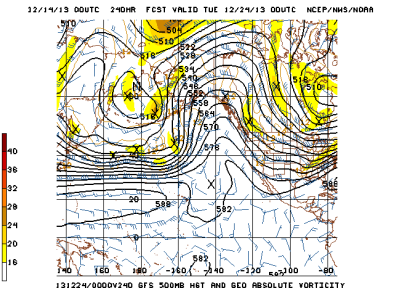
Mar 4, 2019 | California Weather Blog
The extraordinary California dry spell continues: 2013 will probably be the driest year on record
Science Source
| Journal of Climate
Preconditioning of Arctic Stratospheric Polar Vortex Shift Events
Jinlong Huang and Wenshou Tian
Event

Jan 16, 2019
Polar Vortex Split and Eastern US Arctic Invasion January 2019


