Science Source
Diagnosing conditional anthropogenic contributions to heavy Colorado rainfall in September 2013
- States that the Colorado floods of September 2013 caused severe damage and fatalities, and resulted from prolonged heavy rainfall unusual for that time of year
- Investigates the possible role of anthropogenic climate change in this extreme event
- Employs a part dynamical modeling-, part observational-based event attribution approach, which simulates regional Colorado rainfall conditional on boundary conditions prescribed from the observed synoptic-scale meteorology in September 2013 – and assumes these conditions would have been similar in the absence of anthropogenic forcing
- Regional climate model simulations indicate that anthropogenic drivers increased the magnitude of heavy northeast Colorado rainfall for the wet week in September 2013 by 30%, with the occurrence probability of a week at least that wet increasing by at least a factor of 1.3
- Finds that this increase resulted in part from the additional moisture-carrying capacity of a warmer atmosphere – allowing more intense local convective rainfall that induced a dynamical positive feedback in the existing larger scale moisture flow – and also in part from additional moisture transport associated with larger scale circulation change
Related Content
Science Source
| Climatic Change
Increased record-breaking precipitation events under global warming
Jascha Lehmann, Dim Coumou, Katja Frieler
Headline
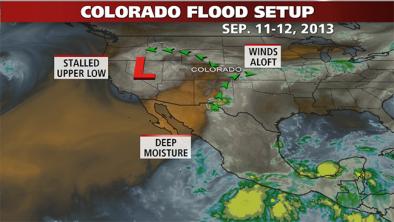
Feb 16, 2016 | The Weather Channel
Colorado Flash Flooding: How It Happened, How Unusual?
Headline

Feb 16, 2016 | Weather Underground
Catastrophic Flood in Boulder, Colorado
Headline

Feb 16, 2016 | Weather Underground
Boulder's 1-in-100 Year Flood Diminishing


