Science Source
EEE 2016: Anthropogenic Forcings and Associated Changes in Fire Risk in Western North America and Australia During 2015/16
Main finding:
Extreme vapor pressure deficits (VPD) have been associated with enhanced wildfire risk. Using one model, we found for 2015/16 that human influences quintupled the risk of extreme VPD for western North America and increased the risk for extratropical Australia.
Open source PDF available here
Larger report:
EEE 2016 = Explaining Extreme Events of 2016 from a Climate Perspective
Related Content
Headline

Jul 22, 2016 | Bloomberg.com
Australia Is Burning, and Climate Change Is Making It Worse
Headline

Jul 22, 2016 | the Guardian
2014 was Australia's third warmest year on record, says Bureau of Meteorology
Headline

Jul 21, 2016 | The Weather Channel
Australian Open Halted Because of Extreme Heat
Headline
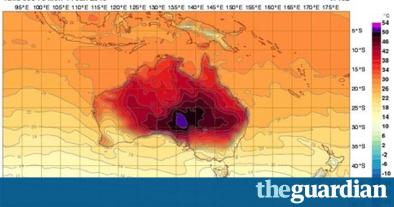
Jul 21, 2016 | the Guardian
Australia adds new colour to temperature maps as heat soars


