Science Source
How much, how fast?: A science review and outlook for research on the instability of Antarctica's Thwaites Glacier in the 21st century
- States that constraining how much and how fast the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) will change in the coming decades has recently been identified as the highest priority in Antarctic research
- Reviews recent research on WAIS and outline further scientific objectives for the area now identified as the most likely to undergo near-term significant change: Thwaites Glacier and the adjacent Amundsen Sea
- Models indicate a potential for greatly accelerated ice loss as ocean-driven melting at the Thwaites Glacier grounding zone and nearby areas leads to thinning, faster flow, and retreat
- Research indicates a complete retreat of the Thwaites Glacier basin would raise global sea level by >3 meters
- Concludes this scenario could occur over the next few centuries, and faster ice loss could occur through processes omitted from most ice flow models such as hydrofracture
- Concludes that increased basal melt at the grounding zone and increased potential for hydrofracture due to enhanced surface melt could initiate a more rapid collapse within the next few decades
Related Content
Headline

Jan 29, 2020 | BBC News
Journey to the 'doomsday glacier'
Headline
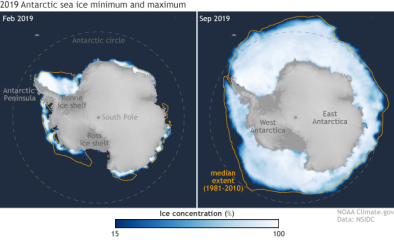
Nov 22, 2019 | NOAA Climate.gov
Understanding climate: Antarctic sea ice extent
Headline

Mar 26, 2019 | The Guardian
Australian researchers find huge lakes beneath largest east Antarctic glacier
Science Source
| Geophysical Research Letters
Mass Loss of Totten and Moscow University Glaciers, East Antarctica, Using Regionally Optimized GRACE Mascons
Yara Mohajerani, Isabella Velicogna, Eric Rignot


