Science Source
More Intense, More Frequent, and Longer Lasting Heat Waves in the 21st Century
- A global coupled climate model shows that there is a distinct geographic pattern to future changes in heat waves
- Observations and the models show that present-day heat waves over Europe and North America coincide with a specific atmospheric circulation pattern that is intensified by ongoing increases in greenhouse gases
- Model results for areas of Europe and North America, associated with the severe heat waves in Chicago in 1995 and Paris in 2003, show that future heat waves in these areas will become more intense, more frequent, and longer lasting in the second half of the 21st century
Related Content
Headline
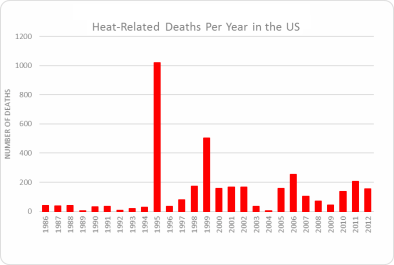
Apr 1, 2016 | Illinois State Climatologist Office
Heat-Related Deaths in the US
Science Source
| Annals of Internal Medicine
Near-Fatal Heat Stroke during the 1995 Heat Wave in Chicago
Jane E. Dematte, Karen O'Mara, Jennifer Buescher et al
Headline

Apr 1, 2016 | Chicago Magazine
How 739 People Died in a Chicago Heat Wave
Science Source
| PubMed - NCBI
Heat waves in the United States: mortality risk during heat waves and effect modification by heat wave characteristics in 43 U.S. communities
Anderson GB and Bell ML


