Science Source
Responses of compound daytime and nighttime warm-dry and warm-humid events to individual anthropogenic forcings
Study key findings & significance
- Greenhouse gases alone amplify the natural frequency of warm-dry events by 1.5-5 times and warm-humid events by 2-9 times in tropical and extratropical latitudes.
- As greenhouse gas emissions are expected to continue impacting our global climate, we expect to see greater frequencies of warm-dry and especially warm-humid events.
- Compound hot and humid conditions are also extremely dangerous for human health and can amplify heat-related morbidity and mortality rates (Raymond et al 2020, Li et al 2020).
Related Content
Headline

Feb 15, 2024 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Amazon Could Reach Tipping Point By Midcentury
Headline

Jan 16, 2024 | Climate Nexus Hot News
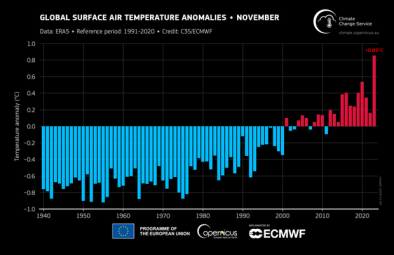
2023 Smashes Hottest Year Record
Headline
Dec 7, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
It’s Official - 2023 Is World's The Hottest Year On Record
Headline

Dec 7, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Earth Veering Closer To Dangerous Tipping Points


