Science Source
Attribution of Declining Western U.S. Snowpack to Human Effects
- Observations show snowpack has declined across much of the western United States over the period 1950–99
- Performs a formal model-based detection and attribution (D–A) study of these reductions
- States that the detection variable is the ratio of 1 April snow water equivalent (SWE) to water-year-to-date precipitation (P), chosen to reduce the effect of P variability on the results
- Obtains estimates of natural internal climate variability from 1600 years of two control simulations performed with fully coupled ocean–atmosphere climate models
- Takes estimates of the SWE/P response to anthropogenic greenhouse gases, ozone, and some aerosols are taken from multiple-member ensembles of perturbation experiments run with two models
- The D–A shows the observations and anthropogenically forced models have greater SWE/P reductions than can be explained by natural internal climate variability alone
- Finds that model-estimated effects of changes in solar and volcanic forcing likewise do not explain the SWE/P reductions
- Finds that the mean model estimate is that about half of the SWE/P reductions observed in the west from 1950 to 1999 are the result of climate changes forced by anthropogenic greenhouse gases, ozone, and aerosols
Related Content
Headline
May 15, 2017 | The Weather Channel
With More Snow on the Way, Some Western Snowpack is Still at Record Mid-May Levels
Headline

May 5, 2017 | Los Angeles Times
Central California towns in trouble if Sierra snowpack melts too fast
Headline

Apr 30, 2017 | The Washington Times via Associated Press
Heat wave melting record snowpack in Northern California
Headline
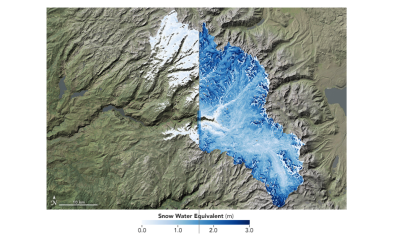
Apr 26, 2017 | Climate Central
California Got More Snow This Winter Than Past 4 Total


