Science Source
Quantifying anthropogenic influence on recent near-surface temperature change
- Assesses the extent to which observed large-scale changes in near-surface temperatures over the latter half of the twentieth century can be attributed to anthropogenic climate change as simulated by a range of climate models
- Rejects the hypothesis that observed changes are entirely due to internal climate variability at a high confidence level independent of the climate model used to simulate either the anthropogenic signal or the internal variability
- Concludes that the influence of anthropogenic greenhouse gases emerges as a substantial contributor to recent observed climate change, with the estimated trend attributable to greenhouse forcing similar in magnitude to the total observed warming over the 20th century
Related Content
Headline

Jan 22, 2020 | Insurance Journal
Natural Disasters in Past Decade Broke Records for Economic, Insured Losses
Headline
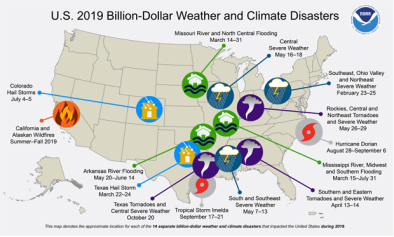
Jan 14, 2020 | ClimateWatch Magazine
2010-2019: A landmark decade of U.S. billion-dollar weather and climate disasters
Science Source
| Nature Climate Change
Climate change now detectable from any single day of weather at global scale
Sebastian Sippel, Nicolai Meinshausen, Erich M. Fischer et al
Headline
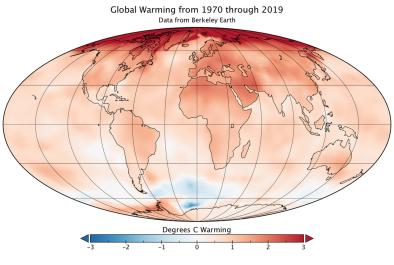
Dec 5, 2019 | Washington Post
The simplest of climate models run decades ago accurately projected global warming


