Science Source
Recent regional climate cooling on the Antarctic Peninsula and associated impacts on the cryosphere
- Examines climate variability since the 1950s in the Antarctic Peninsula (AP) region
- States that this region is often cited among those with the fastest warming rates on Earth
- Re-assesses climate data and finds the data shows a cooling trend initiated around 1998/1999
- States this recent cooling has already impacted the cryosphere in the northern AP
- Observes changes on glacial mass balances, snow cover and permafrost state

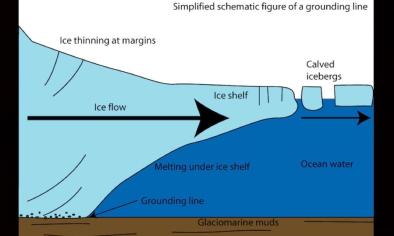
Fig. 1. Location of the AP within the Antarctic continent. b. Detail of the South Shetland Islands and its stations. c. Distribution of the stations on the Peninsula and neighbouring islands, with inter-decadal MAAT variations since 1956 across the AP region.

Fig. 2. Temporal evolution of the MAATs for selected stations, including significant trends at p b 0.05*, p b 0.01**, p b 0.001*** and n.s. (not significant at p N 0.05).
Related Content
Headline
Jul 13, 2017 | Weather Underground
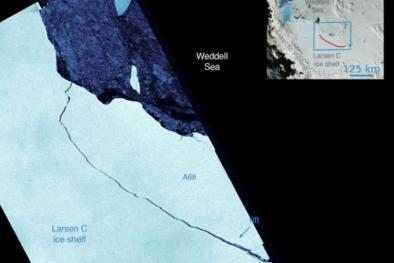
Delaware-Sized Iceberg Detaches from the Larsen C Shelf
Headline
Jul 13, 2017 | Mashable
The 7 best views of the Larsen C iceberg breaking off Antarctica
Headline

Jul 12, 2017 | Mashable
One of the largest icebergs ever recorded just broke free of Antarctica
Headline

Jul 12, 2017 | USA Today
An Antarctic iceberg nearly the size of Delaware — one of the largest on record — has broken off


