Science Source
Externally Forced and Internally Generated Decadal Climate Variability Associated with the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation
- Finds that globally averaged surface air temperatures in some decades show rapid increases (accelerated warming decades), and in other decades there is no warming trend (hiatus decades)
- States that a previous study showed that the net energy imbalance at the top of the atmosphere of about 1 W m−2 is associated with greater increases of deep ocean heat content below 750 m during the hiatus decades, while there is little globally averaged surface temperature increase or warming in the upper ocean layers
- Examines the processes involved with accelerated warming decades and address the relative roles of external forcing from increasing greenhouse gases and internally generated decadal climate variability associated with interdecadal Pacific oscillation (IPO)
- Model results from the Community Climate System Model, version 4 (CCSM4), show that accelerated warming decades are characterized by rapid warming of globally averaged surface air temperature, greater increases of heat content in the upper ocean layers, and less heat content increase in the deep ocean, opposite to the hiatus decades
- Finds that, in addition to contributions from processes potentially linked to Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW) formation and the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC), the positive phase of the IPO, adding to the response to external forcing, is usually associated with accelerated warming decades. Conversely, hiatus decades typically occur with the negative phase of the IPO, when warming from the external forcing is overwhelmed by internally generated cooling in the tropical Pacific
- Finds that internally generated hiatus periods of up to 15 years with zero global warming trend are present in the future climate simulations
Related Content
Science Source
| World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate in 2016
Real Time Data
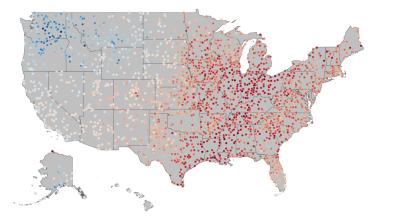
Mar 15, 2017 | Global Historical Climatology Network–Daily (GHCN-D)
US Annual Average Temp as Departure from Normal
Headline
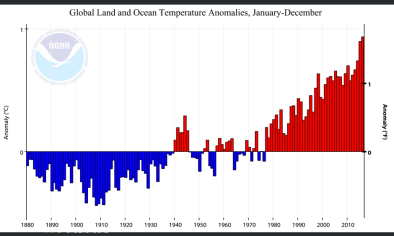
Jan 19, 2017 | Category 6
Confirmed: 2016 the Warmest Year in History of Global Recordkeeping
Headline

Jan 19, 2017 | Los Angeles Times
Wildfires, sea level rise, coral bleaching: Climate change is already here


