Science Source
Attributing extreme fire risk in Western Canada to human emissions
- Canada is expected to see an increase in fire risk under future climate projections. Large fires, such as that near Fort McMurray, Alberta in 2016, can be devastating to the communities affected. Understanding the role of human emissions in the occurrence of such extreme fire events can lend insight into how these events might change in the future
- Uses an event attribution framework to quantify the influence of anthropogenic forcings on extreme fire risk in the current climate of a western Canada region
- Uses fourteen metrics from the Canadian Forest Fire Danger Rating System to define the extreme fire seasons
- Estimates that for the majority of these metrics and during the current decade, the combined effect of anthropogenic and natural forcing have made extreme fire risk events in the region 1.5 to 6 times as likely compared to a climate that would have been with natural forcings alone
Related Content
Headline

Jul 6, 2016 | USA Today
2 months later, massive Canadian wildfire finally 'under control'
Real Time Data
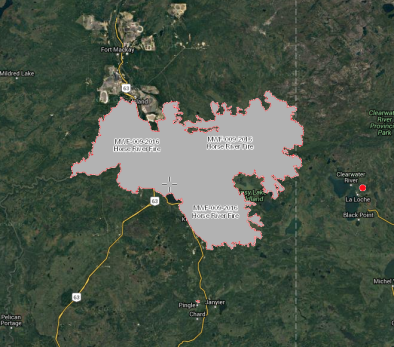
Jun 30, 2016 | PropertyLineMaps / Joseph Elfelt
Alberta Wildland Fires
Headline

Jun 23, 2016 | National Geographic
Forest Fires Can Heat Up the Whole Planet
Headline

Jun 14, 2016 | CBC News
Fort McMurray fire largely contained thanks to rain, firefighters' efforts


