Science Source
Impact of Climate Variability on Runoff in the North-Central United States
- States that large changes in runoff in the north-central United States have occurred during the past century, with larger floods and increases in runoff tending to occur from the 1970s to the present
- States that the attribution of these changes is a subject of much interest
- Uses long-term precipitation, temperature, and streamflow records to compare changes in precipitation and potential evapotranspiration (PET) to changes in runoff within 25 stream basins
- The basins studied were organized into four groups, each one representing basins similar in topography, climate, and historic patterns of runoff
- Precipitation, PET, and runoff data were adjusted for near-decadal scale variability to examine longer-term changes
- A nonlinear water-balance analysis shows that changes in precipitation and PET explain the majority of multidecadal spatial/temporal variability of runoff and flood magnitudes, with precipitation being the dominant driver
- Historical changes in climate and runoff in the region appear to be more consistent with complex transient shifts in seasonal climatic conditions than with gradual climate chang
Related Content
Headline

Mar 25, 2019 | U.S.
Floods shut nearly a sixth of U.S. ethanol production
Headline
Mar 22, 2019 | The Weather Channel
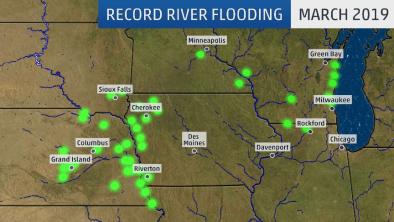
Record Flooding in Nebraska, Iowa, South Dakota, Wisconsin, Minnesota and Illinois Follows Snowmelt, Bomb Cyclone
Headline

Mar 22, 2019 | New York Times
Why Is There Flooding in Nebraska, South Dakota, Iowa and Wisconsin?
Science Source
| Journal of Climate
The Effect of Global Warming on Severe Thunderstorms in the United States


