Science Source
Getting ahead of Flash Drought: From Early Warning to Early Action
Study key findings & significance
- Though recent years have seen tremendous advances in our understanding of this extreme climate phenomenon, substantial work remains to fill scientific gaps and to address the drought early warning and mitigation needs of practitioners and policy-makers.
Abstract
Flash droughts, characterized by their unusually rapid intensification, have garnered increasing attention within the weather, climate, agriculture, and ecological communities in recent years due to their large environmental and socioeconomic impacts.
Related Content
Headline

Oct 26, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
The Planet is ‘Under Siege,’ Scientists Say
Headline

Oct 19, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Amazon Reaches Record Lows
Headline

Oct 11, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Climate Change Forcing Children to Move
Headline
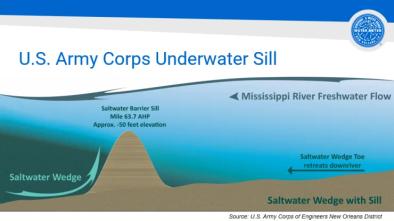
Oct 2, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
NOLA Faces Saltwater Onslaught—And a New Water Crisis
Science Source
Flash Droughts: A Review and Assessment of the Challenges Imposed by Rapid-Onset Droughts in the United States
Study key findings & significance
- The paper highlights recent research on the phenomenon of flash drought and reviews the literature to present the case for a preferred definition.
- Some researchers focus on duration, but Otkin is advocating for a different definition, one that incorporates the concept of a rapidly intensifying drought, focusing on rate of development as opposed to its duration.
Возьмите деньги без лишних вопросов https:
Related Content
Headline

May 23, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Breakthrough Deal Will Help Protect Drought-Stricken Colorado River
Headline

Apr 27, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Catastrophic East Africa Drought Crisis Impossible Without Climate Change
Headline

Apr 19, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Climate Change Making Droughts Faster, More Furious
Headline

Apr 13, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
DOI Issues Colorado River Cuts Options
Science Source
Rapid intensification of the emerging southwestern North American megadrought in 2020–2021
Study key findings & significance
- The Western U.S.
Related Content
Headline

Feb 8, 2023 | Los Angeles Times
Colorado River crisis is so bad, lakes Mead and Powell are unlikely to refill in our lifetimes
Headline

Feb 2, 2023 | CNN
How California’s recent flooding could set the stage for a dangerous wildfire season
Headline

Jan 17, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
California Rains Bring Death, Power Outages
Headline

Jan 17, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Great Salt Lake Will Disappear In 5 Years
Science Source
Assessing the climate-scale variability of atmospheric rivers affecting western North America
Study key findings & significance
- Using a new detection scheme, a 69 yearlong catalog of atmospheric rivers land-falling upon western North America is created and validated
- AR landfalls show a marked seasonal progression from the Gulf of Alaska in the early fall to northern California in early winter
- The seasonal intensity of AR landfalls varies from year to year and from decade to decade in relation to Pacific SST variability
Abstract
A new method for automatic detection of atmospheric rivers (ARs) is developed and applie
Related Content
Science Source
| Geophysical Research Letters
The Shifting Scales of Western U.S. Landfalling Atmospheric Rivers Under Climate Change
Alan M. Rhoades, Andrew D. Jones, Abhishekh Srivastava et al
Event

Oct 25, 2023
California Atmospheric Rivers January 2023
Headline

Apr 13, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Compound Impacts Compound California Threats
Headline

Apr 4, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
California's Lake Tulare Refills, Flooding And Disaster Ensue
Science Source
Human influence has intensified extreme precipitation in North America
Study key findings & significance
- Although previous work has identified an anthropogenic influence on extreme precipitation at hemispheric scales, this study finds robust results for a continental scale.
- The study establishes that anthropogenic climate change has contributed to the intensification of continental and regional extreme precipitation.
- Furthermore, the study shows that the anthropogenic influence on North American regional precipitation will lead to more frequent and intense precipitation extremes in the future.
Autho
Related Content
Headline

Oct 2, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
NYC’s Latest Deluge Dropped a Month's Worth of Rain in Just Hours
Headline

Sep 20, 2023 | CNN
Horrific Libya flooding made up to 50 times more likely by planet-warming pollution, scientists find
Headline

Sep 12, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Quarter Of Libyan City 'Has Disappeared' After Floodwaters Destroy Dams
Headline

Sep 12, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Record 23 Billion-Dollar Disasters in 2023, With Four Months To Go
Science Source
Unprecedented climate events: Historical changes, aspirational targets, and national commitments
Study key findings & significance
- This study expands on previous work analyzing historical climate data, which demonstrated how greenhouse gas emissions have increased the probability of recording-breaking hot, wet and dry events in the present climate.
- Now, the group analyzed similar models to estimate the probability of extreme weather events in the future under two scenarios of the Paris Agreement: increases of 1.5 to 2 degrees
Related Content
Headline

Feb 7, 2024 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Heat And Smoke Are Worse Together Than Apart
Science Source
| Geophysical Research Letters
Spatiotemporal Evolution of Heat Wave Severity and Coverage Across the United States
David Keellings and Hamid Moradkhani
Science Source
| MDPI
The Effects of Historical Housing Policies on Resident Exposure to Intra-Urban Heat: A Study of 108 US Urban Areas
Jeremy S. Hoffman, Vivek Shandas, and Nicholas Pendleton
Headline

Nov 17, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Our Warming World Is Dangerous For Human Health
Science Source
Precipitation Extremes: Trends and Relationships with Average Precipitation and Precipitable Water in the Contiguous United States
Study key findings & significance
- The study finds concurrent increasing trends in extreme precipitation and precipitable water aggregated in large regions of the US.
Гроші надходять на картку негайно https://finpozyka.com.ua/mikrokredyt-na-kartu/ в будь-який момент, без зайвих процедур.
Abstract
Trends of extreme precipitation (EP) using various combinations of average return intervals (ARIs) of 1, 2, 5, 10, and 20 years
Related Content
Science Source
| Climatic Change
Extreme precipitation in the Northeast to increase 52% by the end of the century, study predicts
Christopher J. Picard, Jonathan M. Winter, Charlotte Cockburn et al
Headline

May 9, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Flooding Kills Over 400 In Democratic Republic Of Congo
Headline
Apr 27, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Another South Florida Condo Evacuated
Headline

Apr 19, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Ft. Lauderdale Submerged By 2+ft. Of Rain In 1 Day
Science Source
Cold waves are getting milder in the northern midlatitudes
Study key findings & significance
- The long-term station data have strong decreases everywhere in the lowest minimum temperature.
- Considering the area experiencing cold waves over the last decades, the most notable feature is a sharp decline of this area since the 1980s.
- An analysis of the entire northern midlatitudes confirms the steady decrease in severity and frequency of cold waves over the last decades in the observations.
Related Content
Science Source
Sixfold Increase in Historical Northern Hemisphere Concurrent Large Heatwaves Driven by Warming and Changing Atmospheric Circulations
Study key findings & significance
- The study assesses recent changes in the occurrence of simultaneous large heatwaves.
- The average number of days between May and September with at least one large heat wave in the Northern Hemisphere doubled between the 1980s and the 2010s, to around 152 from 73. But the number of days with two or more heat waves was seven times higher, growing to roughly 143 from 20.
Related Content
Headline

Sep 26, 2023 | NBC News
Underground climate change: How heat is trapped under the surface, threatening buildings
Headline

Sep 26, 2023 | AP
After summer’s extreme weather, more Americans see climate change as a culprit, AP-NORC poll shows
Headline
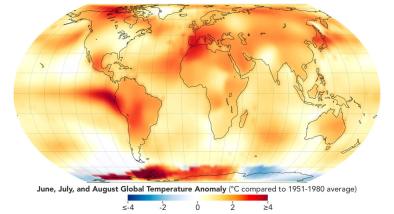
Sep 20, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
NASA + NOAA Confirm This Was The Hottest Summer On Record
Headline

Sep 14, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Historic summer heat highlights AC inequities
Science Source
Diverse Characteristics of U.S. Summer Heat Waves
Study key findings & significance
- For the country as a whole and when evaluated regionally, heat waves are more frequent and show greater persistence when defined using daily maximum versus daily minimum temperatures. This was true for all four of the temperature variables examined, including temperature itself and three variables incorporating atmospheric moisture.
- There are notable regional variations in heat wave occurrence.
- Statistically significant upward trends in the frequency of heat wave occurrence are identified for most U.S.
Related Content
Headline
Aug 10, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Persian Gulf Region Suffers Under Brutal Heat
Headline
Aug 8, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Gulf Heat Shuts Down Oil Refineries
Headline

Aug 3, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Climate Heated July Temps For 81% Of People On Earth
Headline

Aug 1, 2023 | Climate Nexus Hot News
Extreme Heat Exacerbates Intersecting Inequities


