North Atlantic Surface Temperature Decrease
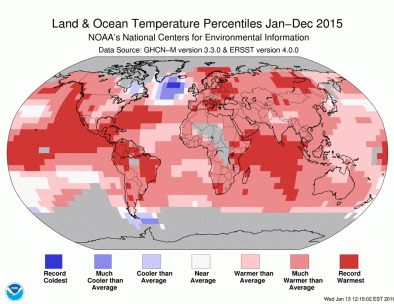
While most of the Earth’s surface shows consistent and rapid warming, there’s a spot in the North Atlantic that stands in marked contrast where recent winters have been characterized by rapid and extreme cooling that’s unprecedented in over 30 years. The cold has been attributed to the slowdown of the Gulf Stream System, and changes in atmospheric patterns.
Read MoreAug 3, 2017 | Nature Climate Change
Arctic sea-ice decline weakens the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation
May 18, 2016 | Geophysical Research Letters
Have anthropogenic aerosols delayed a greenhouse gas-induced weakening of the North Atlantic thermohaline circulation?
May 18, 2016 | American Meteorological Society
Twenty-first century Arctic climate change
Climate science at a glance
- As the global climate warms, isolated cooling trends can still occur, driven by disruption of regional circulation patterns or natural variability.
- Cold and fresh surface and subsurface conditions in the north Atlantic are likely linked to weakening of the Gulf Stream System and unusual atmospheric patterns.
- From the winter of 2013–2014 to 2016, there was a large region of persistently low surface temperatures accompanied by a sharp reduction in ocean heat content in the North Atlantic. The low temperatures in the North Atlantic occurred during a record hot year globally. This event is an area of active research.
North Atlantic temperature trends and climate change
- (Josey et al. 2018): Cold ocean temperature anomalies have been observed in the mid- to high-latitude North Atlantic on interannual to centennial timescales. Air-sea interactions, and anomalous weather patterns, are contributing to this cold anomaly.
- (Smeed et al. 2018): Cold and fresh surface and subsurface conditions in the north Atlantic are linked to weakened transport by the north Atlantic Current and AMOC.[3]
- (IPCC, SROCC, 2019): "Recent relatively cold and fresh surface and subsurface conditions in the north Atlantic have been attributed to anomalous atmospheric forcing or weakened transport by the north Atlantic Current and AMOC, and in turn may have contributed to an intensification of deep convection in the Labrador Sea since 2012."
- (IPCC, AR5, 2013): Such contributions to decreased density of the ocean surface layer in the North Atlantic could act to reduce deep ocean convection there and contribute to a near-term reduction of strength of Atlantic Meridional Ocean Circulation (AMOC). However, the strength of the AMOC can also be modulated by changes in temperature, such as those from changing radiative flux.”[1][2]
Earth Systems Signals
Global warming is causing widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and biosphere.
Heat Signals
The Earth is getting hotter due to human activities that release heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere.
Drought Signals
Climate change is making droughts more likely to occur, and more severe when they do.
Wildfires Signals
Climate change is increasing the size, frequency, intensity and seasonality of wildfires.
Hurricanes Signals
Warmer temperatures increase the rate of water evaporation, which feeds moisture and energy into storms.
Floods Signals
Worsening floods due to climate change are putting a growing number of communities at risk.